Confidential Contract Indemnity Life Insurance

Jason Stolz CLTC, CRPC
At Diversified Insurance Brokers, we understand that some agreements are too sensitive to be publicly disclosed—yet the financial obligations behind them are very real. In certain business, legal, executive, or high-net-worth situations, a contract may involve substantial sums, intellectual property rights, private settlements, performance guarantees, or highly confidential financial arrangements. When one of the obligated parties dies unexpectedly, the financial and reputational fallout can be severe. Confidential Contract Indemnity Life Insurance—structured through specialty contract indemnity solutions and placed with Lloyd’s of London—provides discreet, enforceable funding so that private commitments are honored without public exposure. This type of coverage is not a mass-market product. It is engineered for unique agreements where privacy, precision, and legal enforceability matter just as much as the death benefit itself.
Confidential Contract Indemnity – Lloyd’s of London
Discreet, enforceable protection for private, high-stakes agreements. Structured around your exact contractual terms.
Apply NowConfidential Contract Indemnity Life Insurance exists because traditional carriers often decline, limit, or oversimplify complex private obligations. Standard policies are designed for income replacement or estate liquidity—not for indemnifying a confidential obligation tied to a very specific performance clause, settlement agreement, executive compensation structure, or private business arrangement. In contrast, this coverage is built around the contract itself. The policy amount mirrors the indemnity requirement. Beneficiary structure aligns precisely with the agreement. Ownership and assignment are coordinated with legal counsel. And underwriting is handled with heightened discretion to avoid unnecessary disclosure. For clients already exploring advanced planning such as business loan life insurance, term-to-permanent conversions, or custom executive strategies, confidential indemnity coverage can serve as the final protective layer that ensures the agreement performs exactly as written—even if the key party is no longer alive to fulfill it.
Why does this matter? Because when confidential contracts fail, the damage is rarely limited to money alone. Disputes can trigger litigation, reputational harm, regulatory complications, shareholder conflicts, or the collapse of strategic partnerships. Imagine a private settlement agreement requiring ongoing payments for 15 years. Or a confidential executive retention agreement guaranteeing a payout tied to continued service. Or a performance-based contract where a key individual’s presence is essential to delivery. If death interrupts the arrangement, the surviving party may face significant financial loss without a pre-funded mechanism in place. Confidential Contract Indemnity Life Insurance transforms that risk into certainty. The death benefit becomes the contractual backstop—liquidity delivered precisely when needed, without forcing the disclosure of private terms in a public forum.
This coverage is particularly valuable for executives, closely held business owners, venture capital partners, entertainers, professional athletes, technology founders, and high-net-worth individuals with bespoke agreements. It also applies to undisclosed settlements, structured buyout arrangements not appropriate for public filings, cross-border obligations, and international agreements requiring a neutral, globally recognized marketplace. Lloyd’s of London provides the underwriting flexibility and global reach necessary for these scenarios, while Diversified Insurance Brokers coordinates the structure so that the policy language supports the contract language—not the other way around. For clients already evaluating broader life insurance planning strategies, this solution fits alongside estate planning, business succession, and advanced indemnity structures.
Need Discreet Guidance?
Our advisors work directly with you and your legal team under strict confidentiality protocols.
Request Confidential ReviewThe structuring process begins with a confidential review of the agreement. We evaluate the indemnity obligation, term length, triggering events, jurisdiction, and beneficiary requirements. From there, underwriting focuses on the insured party’s health, financial profile, and insurable interest—handled discreetly to protect sensitive information. Policy design can include term structures aligned to the duration of the contract or permanent designs where obligations extend beyond fixed years. In some situations, layering strategies may be appropriate—combining term coverage with permanent guarantees to mirror staggered contractual obligations. If the contract includes financing components, coordination with strategies like loan protection coverage may also be considered to ensure complete risk management.
Unlike conventional insurance conversations that revolve around family income replacement, this planning discussion centers on enforceability, confidentiality, and alignment with legal documentation. Ownership may sit with an entity, a trust, or a counterparty, depending on contractual language. Beneficiary designations are drafted carefully to match indemnity requirements. Assignments may be used when necessary. International agreements can be accommodated through Lloyd’s global framework. The end result is precision: a policy that functions exactly as the contract intends, delivering funds to the correct party at the correct time, without unnecessary administrative friction.
At Diversified Insurance Brokers, we have decades of experience handling complex, high-value life insurance cases that traditional distribution channels cannot accommodate. From advanced contract indemnity life insurance to executive benefit design and specialty underwriting placements, our focus is alignment and discretion. We coordinate with attorneys, CPAs, and financial advisors to ensure every structural detail supports the client’s objectives. Confidential Contract Indemnity Life Insurance is not about marketing exposure—it is about quiet protection. It exists so that private promises remain enforceable, private agreements remain private, and financial obligations are fulfilled without dispute.
Compare Custom Life Insurance Structures
Use our secure quoter below to explore term and permanent options that may complement confidential indemnity planning.
Related Contract & Advanced Planning Guides
Talk With an Advisor Today
Choose how you’d like to connect—call or message us, then book a time that works for you.
Schedule here:
calendly.com/jason-dibcompanies/diversified-quotes
Licensed in all 50 states • Fiduciary, family-owned since 1980
Confidential Contract Indemnity Life Insurance is a specialized policy designed to fund private contractual obligations if a key party dies unexpectedly. Unlike traditional coverage, it is structured around the exact terms of a confidential agreement and is often placed through contract indemnity life insurance solutions for high-value or sensitive arrangements.
This coverage is commonly used by executives, business owners, high-net-worth individuals, entertainers, and parties to private settlements or undisclosed financial agreements. It can also complement strategies like business loan life insurance when contractual obligations involve financing components.
Traditional life insurance focuses on income replacement or estate planning. Confidential indemnity coverage is engineered specifically to mirror a private contract’s financial terms, ownership structure, and beneficiary requirements. It may also integrate with broader life insurance planning strategies for comprehensive protection.
Yes. These cases are handled with strict discretion. Advisors coordinate directly with you and your legal team, and underwriting is managed carefully to protect sensitive details of the agreement while ensuring enforceability of the policy.
Absolutely. Many clients layer confidential indemnity coverage with term or permanent policies. In some cases, strategies such as converting term to permanent life insurance are used to align with longer contractual time horizons.
About the Author:
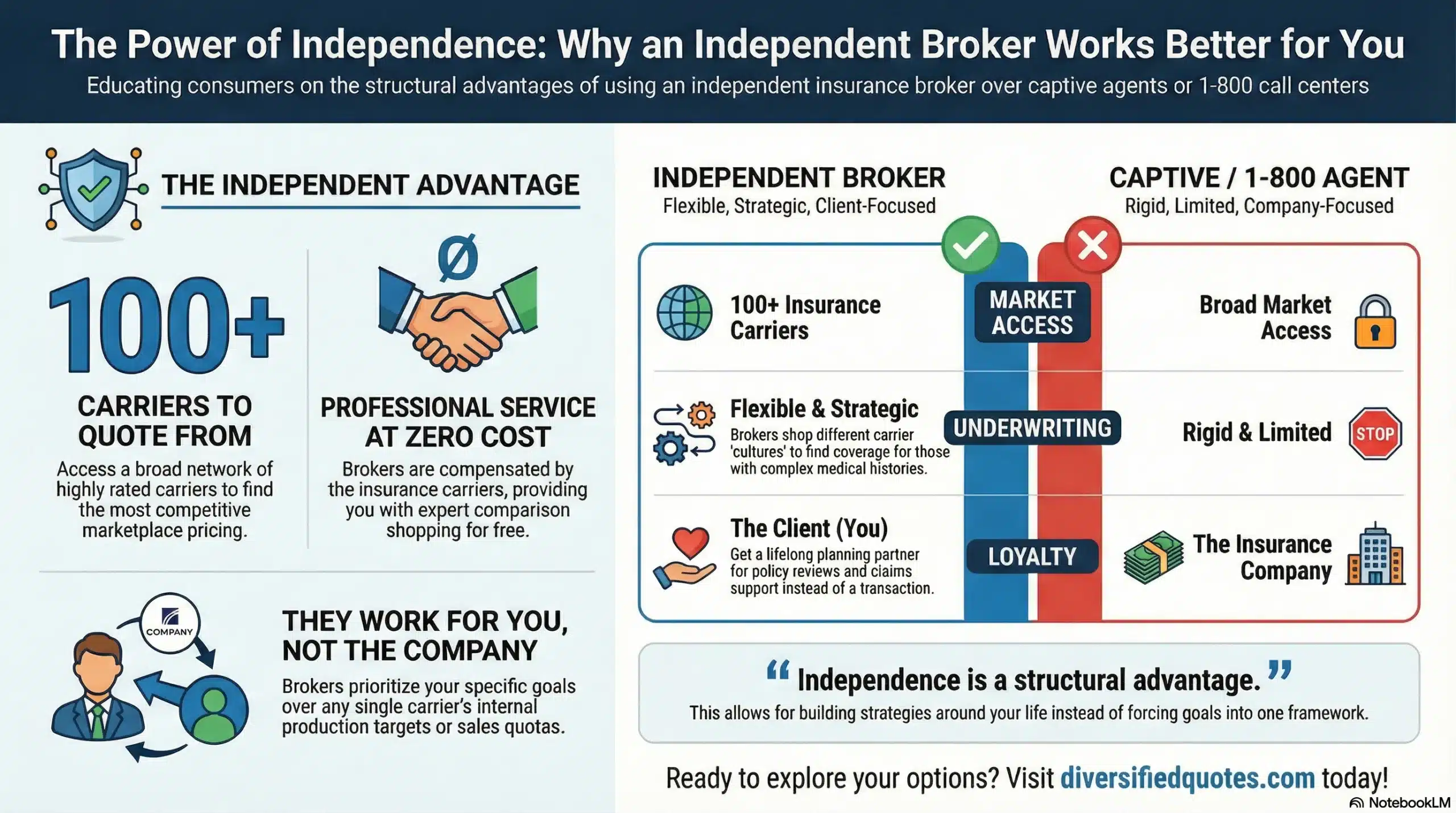
Jason Stolz, CLTC, CRPC and Chief Underwriter at Diversified Insurance Brokers, is a senior insurance and retirement professional with more than two decades of real-world experience helping individuals, families, and business owners protect their income, assets, and long-term financial stability. As a long-time partner of the nationally licensed independent agency Diversified Insurance Brokers, Jason provides trusted guidance across multiple specialties—including fixed and indexed annuities, long-term care planning, personal and business disability insurance, life insurance solutions, and short-term health coverage. Diversified Insurance Brokers maintains active contracts with over 100 highly rated insurance carriers, ensuring clients have access to a broad and competitive marketplace.
His practical, education-first approach has earned recognition in publications such as VoyageATL, highlighting his commitment to financial clarity and client-focused planning. Drawing on deep product knowledge and years of hands-on field experience, Jason helps clients evaluate carriers, compare strategies, and build retirement and protection plans that are both secure and cost-efficient.
